Solving Duplicate Exposure Issues with Tistory Secondary Domains: Strategies to Maintain SEO and Prevent Low-Quality Flags
This guide provides solutions for duplicate page exposure issues between primary and secondary domains on Tistory blogs. We cover how to maintain SEO performance and prevent low-quality blog penalties using proper canonical settings, switching internal URLs to absolute paths, and implementing noindex strategies.
Resolving Low-Quality Blog Penalties and Indexing Issues Caused by Duplicate Exposure
When using a secondary domain on Tistory, the primary domain (.tistory.com) can often be exposed simultaneously, leading to duplication issues. Specifically, if duplicate pages are created due to the primary domain's continued exposure, it negatively impacts SEO performance. To resolve this domain duplication problem, a multi-faceted strategy is required, including proper canonical configuration, changing internal URLs to absolute paths, requesting priority indexing, and implementing noindex settings.
One major issue when using a secondary domain is that both the primary and secondary domains may be indexed by search engines at the same time. This duplicate exposure worsens indexing problems and has a fatal impact on SEO performance. When duplicate pages appear in search results, search engines are likely to evaluate the site's quality as low, which can ultimately lead to a drop in the blog's ranking.
As duplicate pages continue to appear in search results over time, the problem deepens. If left unresolved, the entire blog may eventually be categorized as a low-quality site, leading to a decline in SEO performance and penalties in search results. Therefore, thorough management and proper configuration are essential to eliminate unwanted domain exposure.
The Role of Canonical Tags and the Need for Additional Measures
Importance of Canonical Settings
In the past, duplicate pages occurred frequently because canonical tags were often misconfigured. However, following recent updates, manual modification of canonical settings is generally not required. Nevertheless, a correct canonical tag does not automatically block indexing.
Since search engines may still index the pageviewing the canonical tag as a 'hint' rather than a forced commandadditional technical measures are necessary.
The canonical tag is a crucial 'signal' that tells search engines which URL should be considered the representative page among duplicate content. Even if the Tistory platform has improved this setting, other technical measures such as noindex configurations or absolute path changes must be implemented in parallel to completely block the exposure of the primary domain. This is fundamentally necessary to prevent crawlers from exploring unnecessary paths.
Advanced Strategies for Tistory Secondary Domain Duplicate Page Issues
The Importance of Absolute Internal URL Paths
It is critical to check the internal HTML code and change all URL paths from relative to absolute. When a crawler indexes a site, all URLs connected via relative paths (e.g., `/post/123`) can be interpreted on both the primary and secondary domains, leading to duplicate indexing. If a crawler accesses an unwanted path, the pages linked through that path may also be indexed unintentionally.
Therefore, setting internal URLs as absolute paths, such as 'https://www.example.com/post/123', is an effective way to prevent duplicate pages in advance and clearly inform search engines of the preferred domain. This SEO optimization task must be prioritized when configuring links or image paths within Tistory skin files.

Priority Indexing Requests and Removal of Unnecessary Domains (Via Search Console)
Before indexing occurs through unwanted primary domain paths, you should request indexing for your desired secondary domain path immediately after creating content. This is most effectively done proactively for every new post using the 'URL Inspection' feature in Google Search Console.
This method prevents unnecessary pages from being indexed. Furthermore, if unwanted primary domain URLs have already been indexed, you should request their removal via the 'Removals' tool in Google Search Console. Since this process takes time, taking action as soon as a duplicate issue is identified is vital for preventing low-quality penalties.
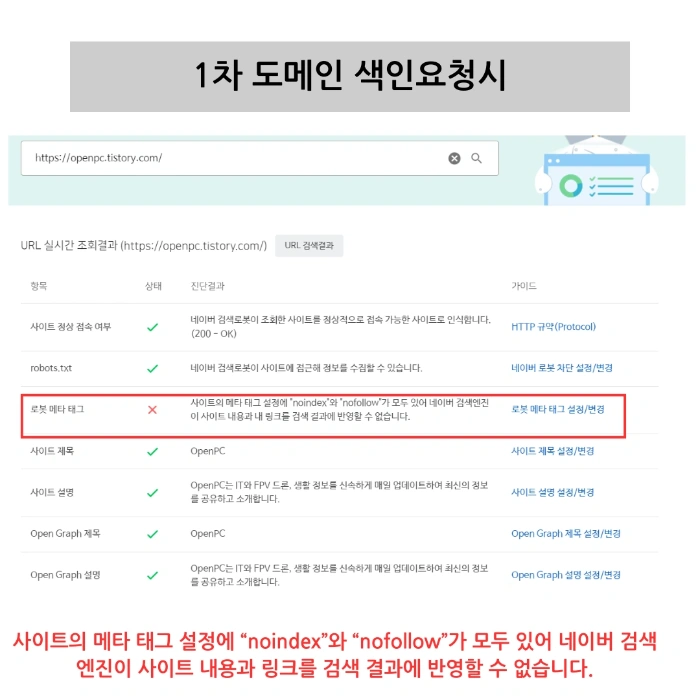
The Most Effective Measure: Utilizing Noindex Settings
The most fundamental and effective method is to block access to the primary domain. If you are willing to concentrate all traffic on the secondary domain, you should implement 'noindex' for the primary domain paths. By inserting a noindex meta tag into the head section of the primary domain's pages, you inform search engines not to display those pages in search results. This fundamentally resolves the Tistory domain exposure issue and ensures SEO performance remains stable.
Q: Why do duplicate page issues occur when using a secondary domain on Tistory?
A: When a secondary domain is applied to a Tistory blog, the original primary domain (.tistory.com) and the secondary domain show identical content on the server. As a result, search engine crawlers may index both domains, creating duplicate pages. This leads to a decline in SEO performance and the risk of the blog being flagged as low quality.
Q: How can I resolve Tistory duplicate domain issues?
A: Resolving duplicate exposure requires a multi-pronged approach: ① Set correct canonical tags. ② Change internal URLs from relative to absolute paths. ③ Request priority indexing for the desired secondary domain. ④ Apply noindex settings or request removal for unnecessary primary domain URLs. These actions guide search engines to index only the correct domain.
Q: Will setting a canonical tag alone solve the duplicate indexing problem?
A: No. While a canonical tag is essential, it is often not enough on its own. Search engines treat the canonical tag as a 'hint,' and may still index duplicate pages. Therefore, additional measures are required, such as using noindex tags to block unwanted paths, utilizing absolute paths to control crawler behavior, and performing removal requests and priority indexing via Google Search Console.